Development of Self-Driving Technology
Using RTAB-Map and SLAM for autonomous navigation of a unmanned ground vehicle for non face-to-face delivery services.
Project Overview
This project focuses on developing an autonomous driving platform technology specifically designed for non-face-to-face delivery services. Motivated by the surge in delivery demand due to COVID-19 and the safety issues associated with motorcycle deliveries, we aimed to create a safe and efficient robot delivery solution.
The system addresses the issue of high delivery fees and minimum order amounts often faced by university students by implementing a “Ride Sharing” concept for delivery items.
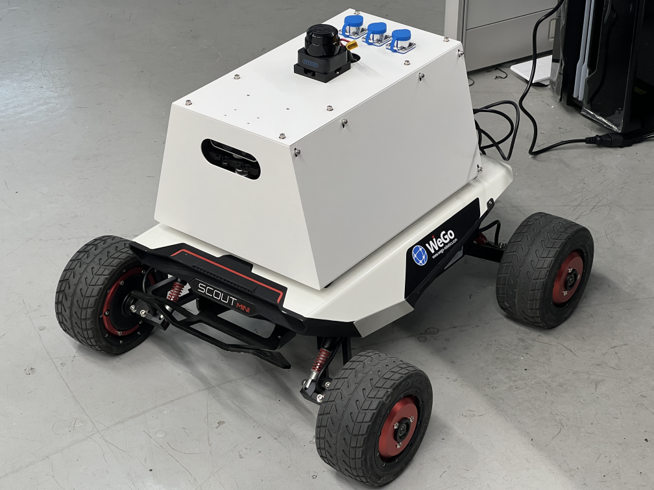 Fig 1. Scout-mini platform equipped with LiDAR and IMU sensors
Fig 1. Scout-mini platform equipped with LiDAR and IMU sensors
Key Features & Objectives
- Autonomous Navigation: Implementing reliable self-driving capabilities using Visual SLAM, Object Detection, and Lane Detection.
- Sensor Fusion: Securing price competitiveness by fusing data from various sensors, including LiDAR and IMU.
- Ride-Sharing Algorithm: A core algorithm designed to optimize delivery routes for multiple orders, reducing costs for the end-user.
System Architecture
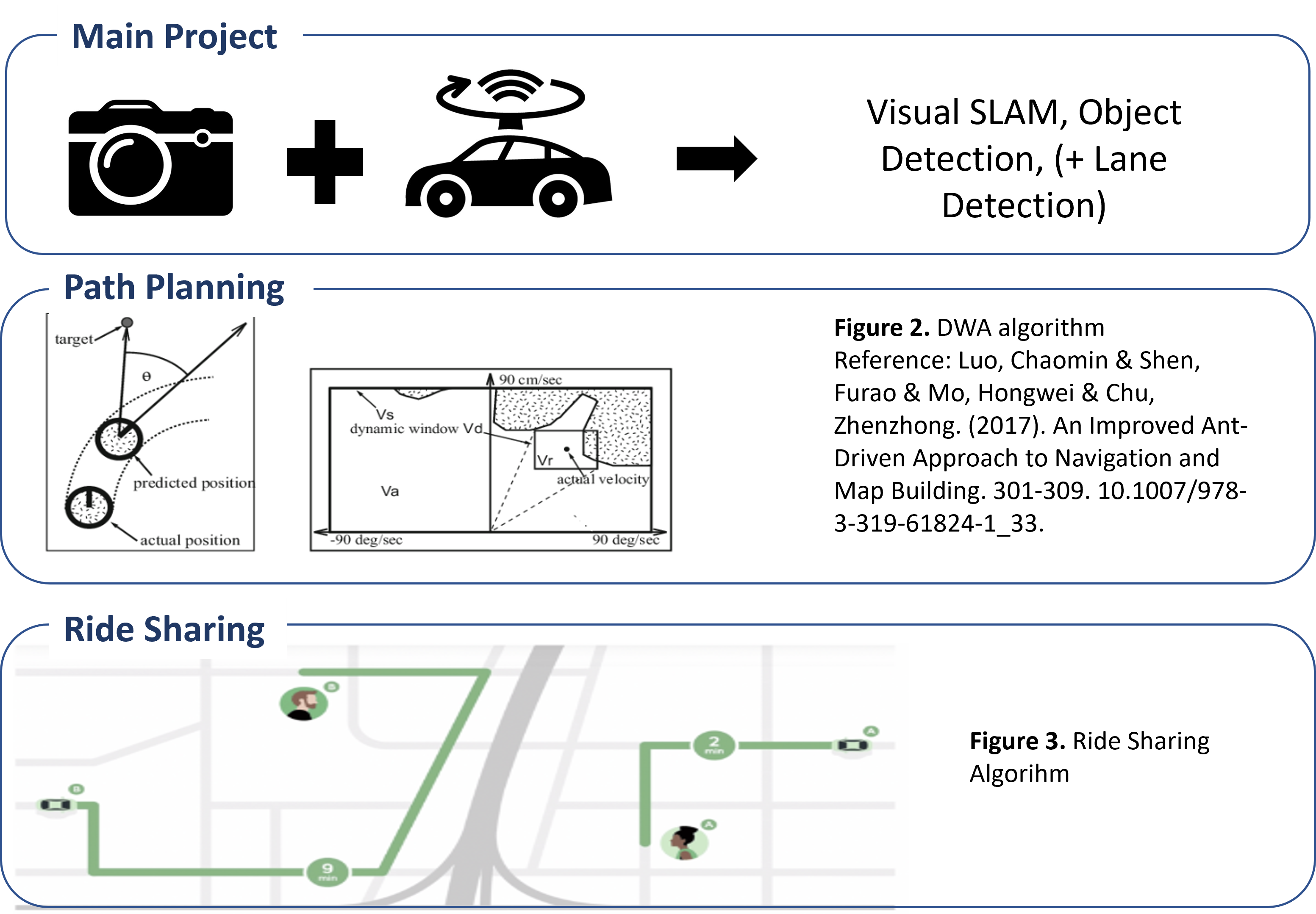 Fig 1. System Architecture
Fig 1. System Architecture
The project was developed using ROS (Robot Operating System) and validated in both simulation and the real world.
- Simulation: We utilized Gazebo to implement and test the main algorithms before real-world deployment.
- Path Planning: The system uses the DWA (Dynamic Window Approach) algorithm for effective obstacle avoidance and navigation.
- Hardware: The platform is built upon the Scout-mini mobile robot base.
Application Development
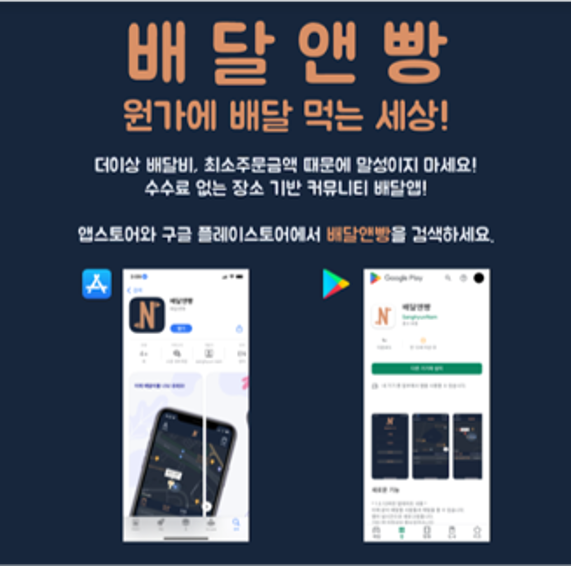 Fig 2. The "N-bbang" delivery community application
Fig 2. The "N-bbang" delivery community application
To complete the service ecosystem, we developed a mobile application named “N-bbang”.
- Function: A location-based community app that allows users to group orders to save on delivery costs.
- Tech Stack: Built using React Native and AWS.
- Integration: The app interlocks with the self-driving robot to coordinate pickup and delivery.
Results
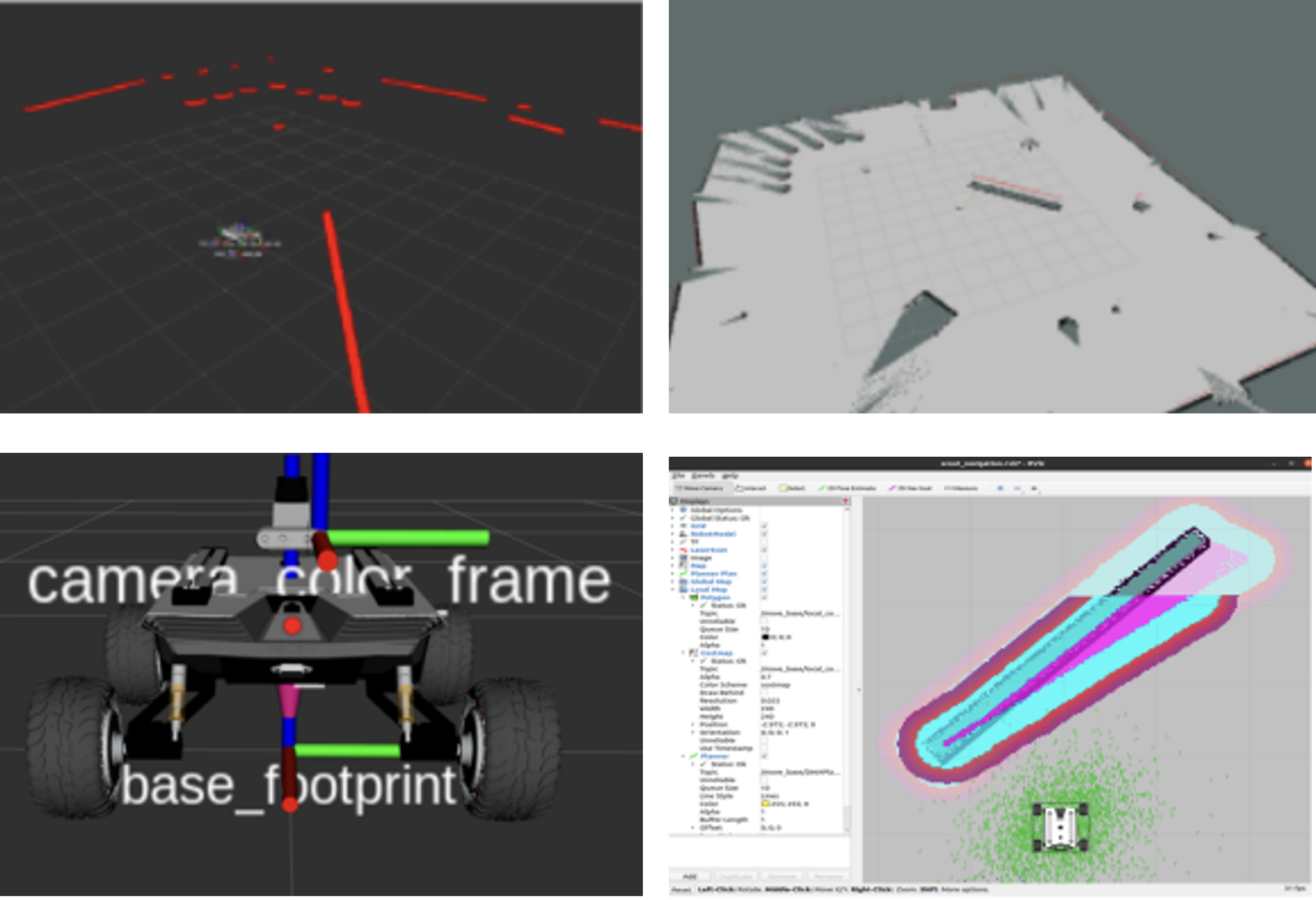 Fig 3. Scout-mini in Gazebo simulator
Fig 3. Scout-mini in Gazebo simulator
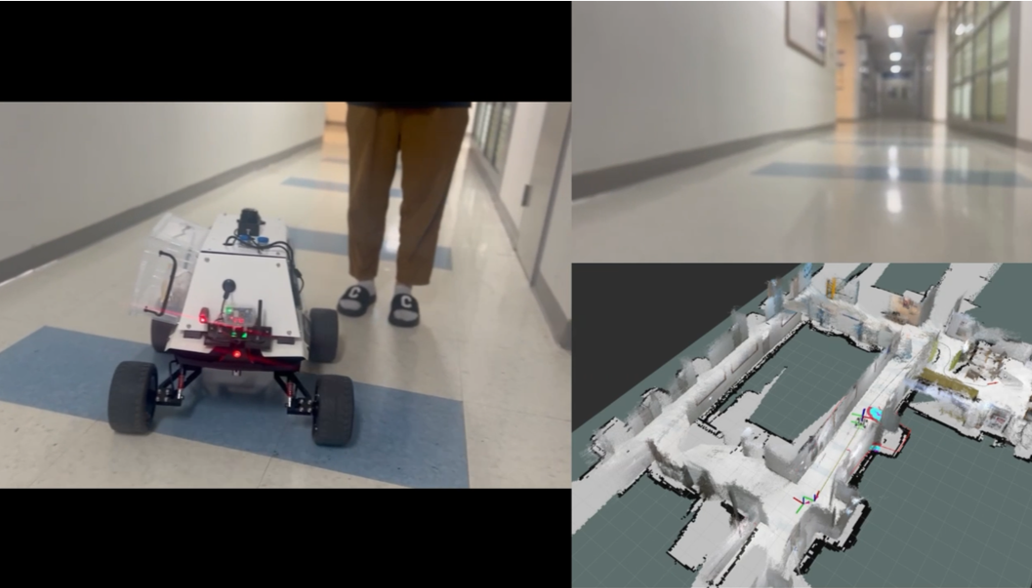 Fig 4. Real-world Scout-mini using RTAB-Map
Fig 4. Real-world Scout-mini using RTAB-Map
Implement the main algorithm using Gazebo simulator and validate the system in the real world.
Acknowledgement
This project was conducted as part of the Internship at UNIST RML / UNIST Brain-To-Society Contest.