Simulator for Multi Agent
A simulation environment for benchmarking path planning algorithms and sensor performance for multi-agent systems.
Duration: 2025.06 - 2025.11
Project Overview
This project involves the development of a Multi-Agent Simulation Environment designed to evaluate and compare the performance of various path planning algorithms and sensor configurations. The primary goal was to analyze how different optimization algorithms and sensor types (Camera, LiDAR) affect the detection rate of targets in a simulated environment.
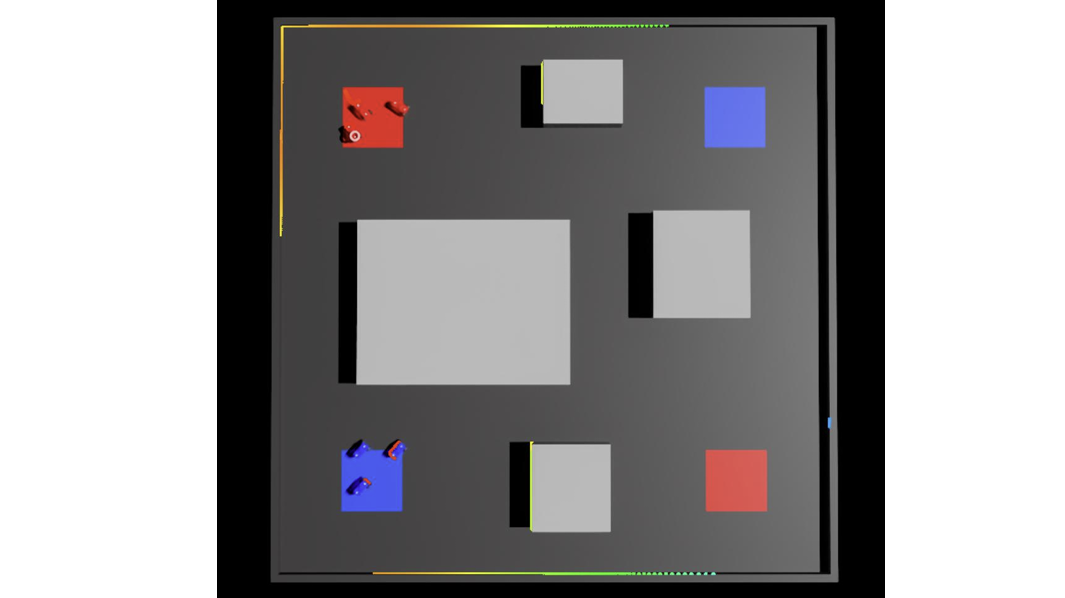 Fig 1. Simulation interface for comparing path planning algorithms
Fig 1. Simulation interface for comparing path planning algorithms
Key Features
1. Path Planning Algorithms Comparison
The simulator implements and benchmarks several deterministic and probabilistic path planning algorithms to navigate agents efficiently.
- Implemented Algorithms:
- A* (A-Star): Evaluated for optimal pathfinding in static environments.
- Dijkstra: Used as a baseline for shortest-path calculation.
- RRT* (Rapidly-exploring Random Tree Star): Tested for high-dimensional configuration spaces and asymptotic optimality.
- Analysis: Comparison of path length, computation time, and safety margins for each algorithm.
2. Sensor Simulation & Detection Analysis
The system simulates various sensor modalities to analyze target detection capabilities.
- Sensor Models:
- Camera: Simulates Field of View (FoV) and visual occlusion.
- LiDAR Point Cloud: Simulates laser scanning for distance measurement and object recognition.
- Performance Metrics: The simulator measures enemy detection rates based on the agent’s movement path and sensor coverage, identifying the most effective sensor placement and path strategies.
System Workflow
- Environment Setup: Load map data (occupancy grid) and configure obstacle placement.
- Configuration: Select the path planning algorithm (e.g., A, RRT) and sensor type (Camera/LiDAR) for the agents.
- Simulation & Logging: Execute the simulation to track agent movements. The system logs detection events and navigation metrics in real-time.
- Evaluation: Analyze the collected data to determine which algorithm and sensor combination yields the highest detection probability and navigation efficiency.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the KAIST Eulji Research Center.